In the landscape of modern C++ programming, smart pointers are indispensable tools that significantly simplify memory management, one of the most challenging aspects of the language. Among these, shared_ptr, introduced in C++11, stands out as a robust and flexible solution for managing dynamically allocated memory. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of shared_ptr, exploring its functionalities, use cases, and best practices.
What is shared_ptr?
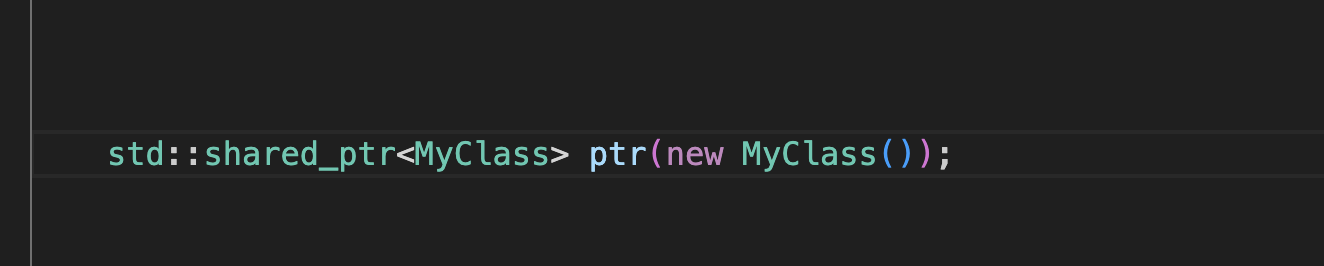
shared_ptr is a smart pointer template provided by the C++ Standard Library, which maintains reference counts for the allocated memory. It automatically deallocates the memory when no more shared_ptr objects point to it. This mechanism effectively addresses the issues of memory leaks and dangling pointers, common pitfalls in manual memory management.
Key Features of shared_ptr
- Automatic Memory Management:
shared_ptrhandles the allocation and deallocation of memory automatically, reducing the risk of memory leaks. - Reference Counting: It keeps track of how many
shared_ptrinstances are associated with a particular memory resource. When the count drops to zero, the memory is freed. - Copy Semantics:
shared_ptrcan be copied safely, as each copy participates in reference counting. - Thread Safety: The reference counting mechanism in
shared_ptris thread-safe in most implementations.
How to Use shared_ptr

Advantages Over Raw Pointers
- Safety:
shared_ptrsignificantly reduces the risk of memory-related errors. - Ease of Use: It simplifies memory management code, making it more readable and maintainable.
- Flexibility: It can be used with custom deleters, allowing for greater control over how memory is deallocated.